Ruixiang Sun, Hongyu Zang, 01 May 2024
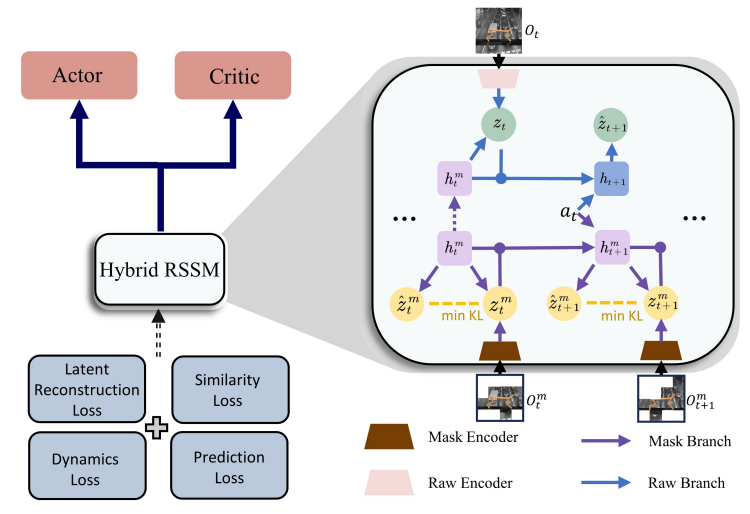
In the cooperation of our lab and DreamFold AI, we designed a novel Visual Model-Based Reinforcement Learning (MBRL) approach to address the issue of non-essential noise in pixel-based observations by applying a spatio-temporal masking strategy and a bisimulation principle, enabling the world model to effectively capture endogenous, task-specific features. Furthermore, we developed a Hybrid Recurrent State-Space Model (HRSSM) structure to enhance state representation robustness, resolving instabilities commonly encountered during the joint training of representations, dynamics, and policy.
Visual MBRL promises to encapsulate agent's knowledge about the underlying dynamics of the environment, enabling learning a world model as a useful planner. However, top MBRL agents such as Dreamer often struggle with visual pixel-based inputs in the presence of exogenous or irrelevant noise in the observation space, due to failure to capture task-specific features while filtering out irrelevant spatio-temporal details.
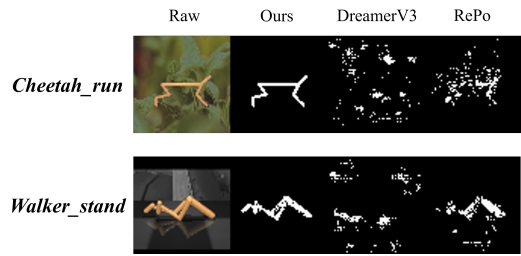
To tackle this problem, we apply a spatio-temporal masking strategy, a bisimulation principle, combined with latent reconstruction, to capture endogenous task-specific aspects of the environment for world models, effectively eliminating non-essential information. Joint training of representations, dynamics, and policy often leads to instabilities. To further address this issue, we develop a Hybrid Recurrent State-Space Model (HRSSM) structure, enhancing state representation robustness for effective policy learning. Our empirical evaluation demonstrates significant performance improvements over existing methods in a range of visually complex control tasks such as Maniskill with exogenous distractors from the Matterport environment.
